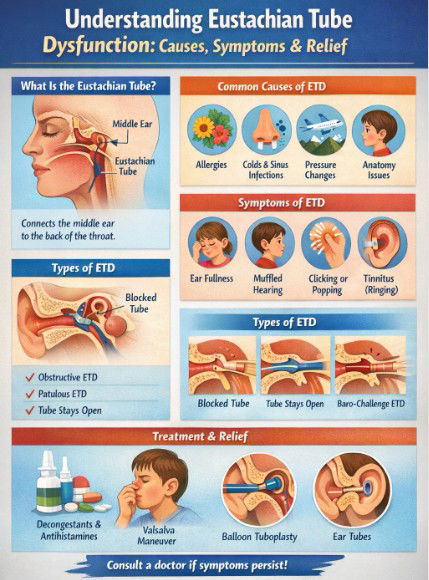
Causes, Symptoms & Relief If you’ve ever felt your ears suddenly “plug up” during a flight, or heard crackling sounds when you swallow, you’ve experienced what happens when your Eustachian tubes aren’t working properly. For most people, this feeling is temporary. But when it becomes persistent, it may be a condition known as Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD). This common issue affects children and adults alike and can range from mildly annoying to significantly disruptive. Here’s what you need to know. What Is the Eustachian Tube? The Eustachian tube is a narrow passageway that connects the middle ear to the back of the throat (near the nasal cavity).
Its key roles are to:
- Regulate and equalize ear pressure
- Drain fluid from the middle ear
- Ventilate the ear space
When this tube becomes blocked, inflamed, or fails to open and close as it should, ETD occurs. Common Causes of ETD Several factors can interfere with the normal function of the Eustachian tube: 1. Allergies Seasonal or environmental allergies can cause inflammation and congestion in the nasal passages, which also affect the tube openings. 2. Upper Respiratory Infections Colds and sinus infections often cause swelling and excess mucus that can block the tubes. 3. Rapid Pressure Changes Changes in altitude (flying, scuba diving, mountain travel) can overwhelm the tube’s ability to equalize pressure. 4. Anatomical Factors Children have smaller, more horizontal Eustachian tubes, making them more prone to dysfunction.
Adults may also have structural issues that contribute (e.g., enlarged adenoids). 5. Chronic Sinus Problems Long-term sinus inflammation can impact tube function. Symptoms of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction ETD symptoms can range from subtle to quite uncomfortable. These may include:
- Ear fullness or pressure
- Muffled or “underwater” hearing
- Clicking, popping, or crackling sounds
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ear)
- Dizziness or imbalance
- Mild ear pain
- Feeling like your ears won’t “pop”
Symptoms may worsen during altitude changes or after illness. Types of ETD There are a few variations:
- Obstructive ETD - The tube is blocked due to mucus or inflammation.
- Patulous ETD - The tube stays abnormally open, causing an echo-like sensation of hearing your own breathing or voice.
- Baro-Challenge ETD - The tube only malfunctions during pressure changes, such as flying or diving.
How Is ETD Diagnosed? A healthcare professional typically evaluates symptoms through:
- Examination of the ears, nose, and throat
- Hearing tests (audiometry)
- Tympanometry (measures middle ear pressure)
Diagnosis helps determine whether the dysfunction is temporary or linked to an underlying condition. Treating and Managing ETDAt-Home Measures
- Swallowing, yawning, or chewing gum to help open the tubes
- Valsalva maneuver (gently blowing while pinching your nose — only if recommended)
- Warm compresses over the ears
- Staying hydrated
Medical Treatments Depending on the cause:
- Antihistamines or nasal corticosteroid sprays for allergies
- Decongestants (short-term use only)
- Treatment for sinus infections
- Autoinflation devices prescribed by clinicians
Procedures (for chronic ETD) In persistent cases:
- Balloon Eustachian Tuboplasty (a minimally invasive procedure to open the tubes)
- Ear tubes (tympanostomy) may be recommended in some situations
Always consult a medical professional before starting treatment, especially if symptoms worsen or persist. When to Seek Medical Care Seek professional evaluation if you experience:
- ETD symptoms lasting longer than a few weeks
- Significant ear pain
- Persistent hearing changes
- Frequent ear infections
- Dizziness or vertigo
Early evaluation can help prevent complications